A water softener removes minerals using ion exchange. Resin beads attract calcium and magnesium, exchanging them for sodium or potassium.
Water hardness, caused by minerals like calcium and magnesium, poses a problem for many households, leading to scale buildup and reducing the efficiency of soaps and detergents. To mitigate this issue, water softeners have become a go-to solution, providing a multitude of benefits ranging from prolonged appliance life to smoother skin and hair.
The process hinges on the simple yet effective principle of ion exchange. With the aid of resin beads contained within the unit, water softeners systematically trade ‘hard’ minerals for ‘soft’ ones, ensuring that the water flowing through your pipes and fixtures is gentler on everything it touches. This introduction serves as a gateway to understanding the essential steps that make soft water a reality in millions of homes.
Introduction To Water Softening
Introduction to Water Softening is your gateway to understanding how to improve your home’s water quality. The minerals in hard water, such as calcium and magnesium, can cause problems with your plumbing and make cleaning difficult. Water softeners tackle these problems by removing the culprits behind these issues.
Overview Of Hard Water And Its Effects
Hard water contains a high mineral content. It leaves scale deposits that can damage appliances, dull your laundry, and affect your skin and hair. Below are common issues:
- Clogged Pipes: Scale build-up reduces water flow and efficiency.
- Appliance Damage: Heaters and washers wear out sooner.
- Faded Clothes: Fabrics lose softness and color quickly.
- Skin and Hair: They become dry and lifeless.
- Extra Expenses: Increased energy bills and repairs.
Basic Principles Of Water Softening
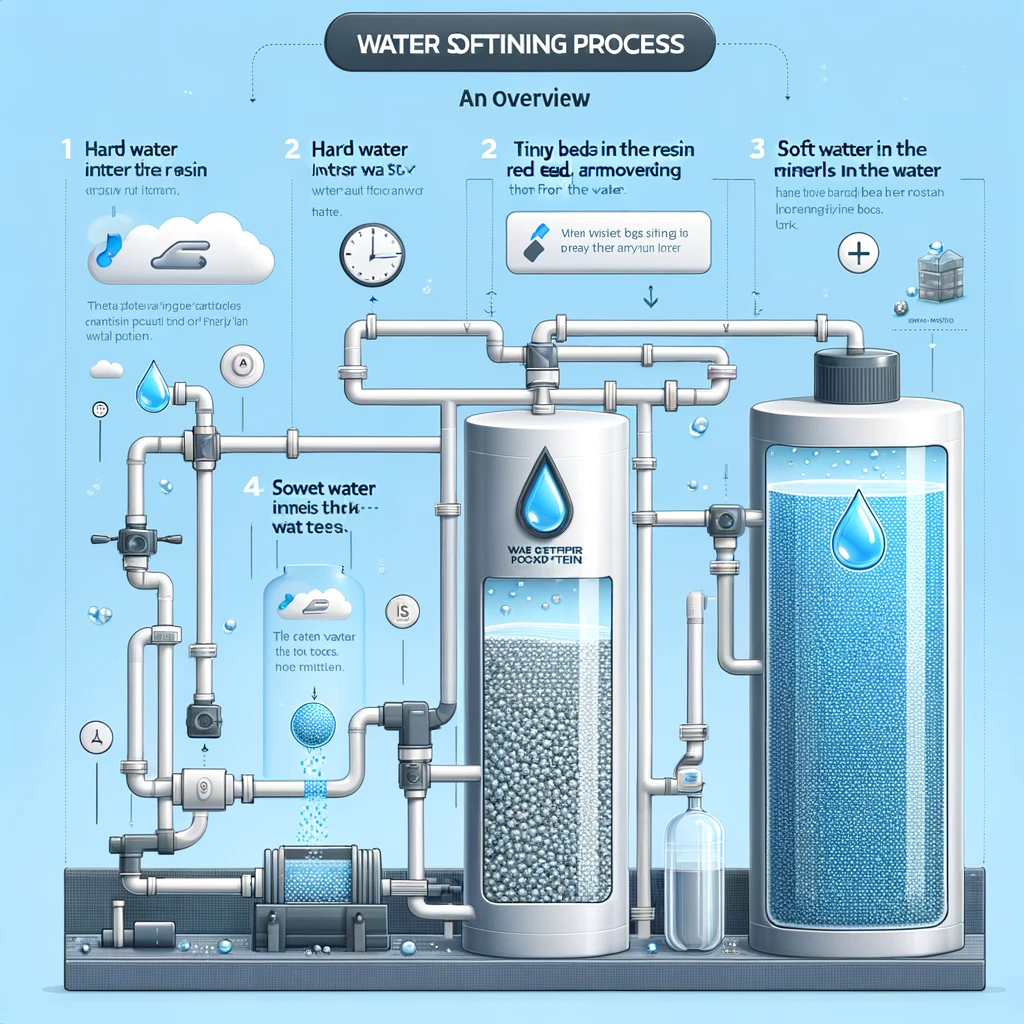
The water softening process uses a method known as ion exchange. This system swaps hard minerals for sodium or potassium ions. Here is the step-by-step breakdown:
- Softening Material: Resin beads in the tank are key players.
- Ion Exchange: Hard minerals swap places with sodium or potassium.
- Regeneration: After saturation, the system must renew its beads.
- Backwash: The unit reverses water flow to clean out sediment.
- Recharge: Brine solution restores the ion content of the beads.
- Rinse: Excess brine and minerals get flushed away.
Understanding Hard Water
Before exploring how a water softener brings purity to our lives, let’s delve into the nature of hard water. Knowing what makes water hard is the first step to understanding how a water softener accomplishes its task.
Definition And Causes Of Hard Water
Hard water is water filled with minerals. These minerals come from rocks and soil. They dissolve in water as it moves through the Earth. The most common minerals in hard water are calcium and magnesium. A lot of hard water comes from areas with limestone and chalk.
Common Minerals That Make Water Hard
- Calcium (Ca2+): From limestone and gypsum.
- Magnesium (Mg2+): From dolomite and other minerals.
- Iron (Fe2+): Less common, but it can stain fixtures with a reddish hue.
Implications Of Hard Water On Daily Life
Hard water can be a nuisance. It affects many things in our homes. Here are some issues it can cause:
| Area Affected | Problems Caused |
|---|---|
| Appliances | A build-up of scale can shorten life. |
| Pipes | Blockages from mineral deposits. |
| Skin and Hair | Dryness and dullness due to residue. |
| Laundry | Less effective cleaning; fabrics feel rough. |
| Dishes | Spots and streaks left after washing. |
Understanding these hardships sets the stage to appreciate the relief a water softener provides.
Components Of A Water Softener
Understanding the components of a water softener is crucial to grasp how it transforms hard water into soft water. Each part plays a pivotal role in this complex process. We will explore the key components one by one.
Mineral Tank Function And Maintenance
At the heart of a water softener lies the mineral tank. This is where the main water-softening process occurs. The tank is filled with resin beads that attract and hold onto minerals like calcium and magnesium, which make water hard.
Maintenance of the mineral tank is straightforward. Regularly check for any sediment build-up or resin bead depletion. Replace the beads when they no longer soften the water effectively.
Control Valve Mechanics And Settings
Regeneration begins when the control valve detects the amount of water passing through the mineral tank. This valve is the brain of the water softener, ensuring optimal performance.
- Settings on the valve can be adjusted to suit the hardness of the incoming water.
- Time and water flow can also be set according to your household’s needs.
Brine Tank And Salt Storage
The brine tank and mineral tank work together. Salt or potassium is used to recharge resin beads in the mineral tank by holding a highly concentrated solution.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Brine Tank | Stores salt and mixes with water to make brine |
| Salt Storage | Keeps salt for the brine solution; regular filling is essential |
Keep the salt level in the brine tank at least half full for continuous softener operation. Be sure to use the type of salt recommended by your softener’s manufacturer for optimal results.
Pre-softening Step: Water Analysis
Understanding the quality of your water is the first step in the journey to softer water.
Before diving into the intricacies of a water softener, it’s crucial to evaluate the water needing treatment.
The process begins with a thorough water analysis.
Testing For Hardness
Recognizing hard water at your home demands a simple, yet effective, test. This test determines the concentration of calcium and magnesium, pinpointing the hardness level.
Professional kits offer detailed results. DIY test strips also serve as a quick check method.
Identifying Mineral Content
Beyond calcium and magnesium, water contains other minerals. A comprehensive analysis includes testing for iron, manganese, and pH levels.
These findings are critical for selecting the right softener.
Adapting Water Softener Settings
Custom settings on your water softener ensure peak performance. These settings are tailored based on the test results from earlier steps.
Optimizing regeneration cycles and salt usage improves both efficiency and longevity.
| Hardness Level (GPG) | Recommended Softener Setting |
|---|---|
| 0 – 3.5 | Low |
| 3.6 – 7.0 | Medium |
| 7.1 – 10.5 | High |
| 10.6+ | Very High |
Step-by-step Water Softening Process
If you’ve ever wondered why your home’s water feels slippery after a shower or leaves spots on dishes, hard water is likely the culprit. Installing a water softener can combat these issues. Let’s dive into how a water softener works from the moment water flows into the system to when it emerges as soft water.
Step 1: Water Entry And Initial Filtration
As water enters the softener, it goes through a stage referred to as initial filtration. This step removes large particles such as sand and sediment. The cleaner water then moves to the next phase, ensuring only finer minerals reach the core softening area. Filters vary, so replacements depend on water usage and quality.
Step 2: Ion Exchange Process
The core of the water softening journey is the ion exchange process. Hard water contains high levels of calcium and magnesium. These are exchanged for sodium ions or sometimes potassium ions. Resin beads inside the softener attract and hold onto the hard minerals, allowing the exchange to occur. This exchange softens the water.
Step 3: Flushing Hard Minerals With Brine Solution
Over time, the resin beads become saturated with hard minerals. A brine solution flushes these minerals away. Salt or potassium chloride in the brine tank mixes with incoming water to form this solution. It cleanses the resin beads, ensuring their effectiveness. Then, hard minerals and excess brine drain out, and the system resumes the softening process.
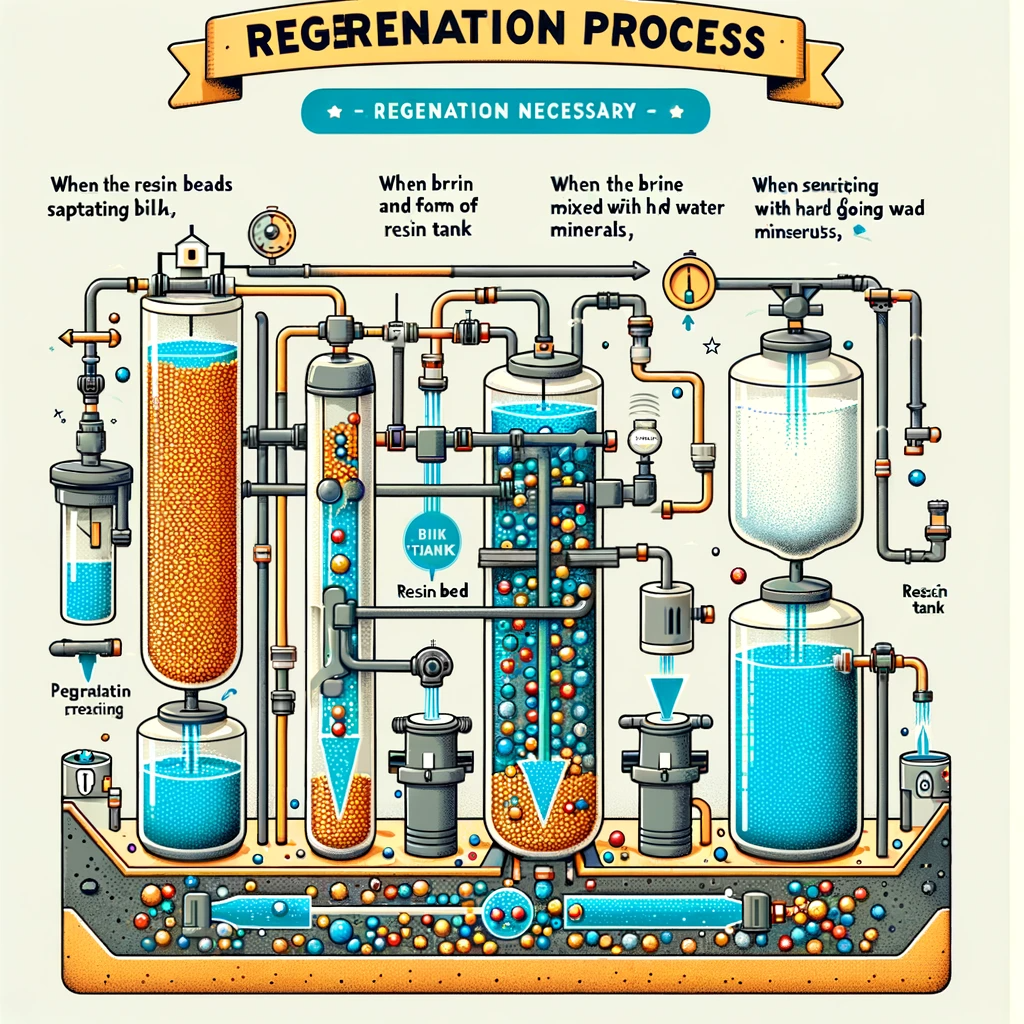
Regeneration Cycle
Every water softener has a secret hero that keeps it running efficiently: the Regeneration Cycle.
This vital process rejuvenates the softener’s resin beads, which are responsible for trapping hard minerals from your water. Without regeneration, the system would cease to soften water.
Understanding The Regeneration Cycle
Regeneration is a multi-step process that cleanses resin beads in your water softener. Think of it as hitting the reset button.
- The system draws brine, a strong saltwater solution, from the brine tank.
- Brine flows through the resin tank, dissolving collected minerals.
- Flushed-out minerals and brine exit through a drain.
- The resin tank gets rinsed with fresh water, prepping it for more softening.
The entire cycle ensures your water softener works at peak performance.
Automatic Vs. Manual Regeneration
Automatic regeneration systems are smart and self-sufficient.
- They track water usage and trigger regeneration as needed.
- No guesswork is involved; convenience is key.
Manual systems, on the other hand, require user intervention. You must initiate the regeneration manually, based on schedule or necessity.
Maintenance And Salt Replenishment
Maintenance is critical for both automatic and manual systems.
- Regularly check the salt levels in the brine tank.
- Refill the salt as needed, ensuring it’s the correct type for your system.
Remember, clean salt prevents impurities from affecting your system’s efficiency.
Schedule maintenance checks to spot potential issues early.

Post-softening Water Quality
Once your water softener has worked its magic, what’s next? Understanding and maintaining newly-softened water becomes a top priority. It’s essential to know if your softener is effective and to spot potential problems early. This section dives into the essentials of post-water softening quality.
Testing For Softness
After the softening process, testing your water is crucial to confirm its softness.
- Test strips or kits can determine water hardness.
- Follow the instructions closely for accurate results.
Assessing The Effectiveness Of The Softener
Soft water should be free of calcium and magnesium — the culprits of water hardness.
Monitor for changes in:
- Limescale buildup on appliances
- Soap and shampoo lathering quality
- Overall water feels during cleaning
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the softener isn’t performing, it’s time to troubleshoot. Issues could range from minor to major.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Hard water spots | Unit malfunction or settings need adjustment | Check settings or contact a professional |
| Resin beads degradation | Can occur from chlorine damage or age | Replace resin beads |
| Excessive salt usage | Possible regeneration cycle error | Reset regeneration frequency |
Environmental And Health Considerations Of Softened Water
Understanding the environmental and health considerations is vital when discussing water softeners. While these devices provide clear benefits in reducing mineral buildup, their operation and by-products warrant a closer look. Specifically, considering their implications for personal health and the wider environmental impact is fundamental.
Sodium Content And Health Impacts
Water softeners typically use sodium to replace hardness minerals like calcium and magnesium. An important aspect to consider is the increase in sodium levels within the softened water. For individuals on a low-sodium diet or with certain health conditions, this could have implications. It is essential to understand how the sodium content in softened water can affect health and nutrition.
- Increased sodium intake for individuals with hypertension
- Possible complications for those with heart or kidney problems
- Evaluation of alternative sodium-free softener options
Environmental Impact Of Brine Discharge
The regeneration cycle of a water softener produces brine waste that has a high salt concentration. This brine is often discharged into sewer systems or septic tanks, which can lead to environmental challenges:
| Impact Area | Potential Effects |
|---|---|
| Soil Saturation | Reduced soil percolation, affecting local vegetation |
| Water Pollution | Risks to aquatic ecosystems due to increased salinity |
| Water Treatment | Challenges in municipal treatment facilities in handling high-salt wastewater |
Alternatives To Conventional Water Softeners
Considering the potential issues posed by traditional water softeners, exploring alternatives is beneficial. These alternatives aim to soften water without the drawbacks of high sodium content and brine discharge.
- Template Assisted Crystallization (TAC) systems
- Magnetic or electronic water conditioners
- Chelation systems, which use agents like citric acid
Each option carries its own set of benefits and limitations, making research and professional advice critical when selecting a suitable water-softening system.
Ensuring Sustained Performance
Understanding the minute details of how water softeners work can be quite enlightening. But, it’s the regular maintenance and timely upgrades that assure the system’s longevity and efficacy. Now, let’s steer towards the essential practices to keep the softener functioning flawlessly.
Best Practices For Maintaining A Water Softener
- Regularly check the salt levels and replenish as needed.
- Clean the brine tank annually to prevent salt bridges and mushing.
- Use the right type of salt – either evaporated or solar salt is recommended.
- Schedule a professional inspection every few years to spot potential issues early.
When To Replace Your Water Softener
Consider replacement if you notice any of these signs:
| Signs | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Changes in water quality | Test water and consult experts |
| Increased salt usage | Check for inefficiencies |
| System age over 15 years | Evaluate new models |
| Constant malfunctions | Compare repair vs. replacement costs |
Final Thoughts On The Importance Of Water Quality
Superior water quality is crucial for health, plumbing, and appliances. A well-kept softener ensures this quality consistently without fail. Embrace best practices, stay vigilant for replacement signs, and enjoy the benefits of soft water every day.
Frequently Asked Questions On How Does A Water Softener Work Step By Step?
What Are The 5 Stages Of The Water Softener Process?
The five stages of the water softener process are 1. Pre-filtration removes large particles 2. Resin beads exchange ions, softening water 3. Brine solution regenerates resin beads 4. Resin tank flushes excess brine 5. Rinsed resin beads ready for the next cycle
What Are The Steps In The Water Softener Process?
The water softener process involves five steps: identification of hard water, selecting a suitable softener, installation, ion exchange to remove minerals, and periodic regeneration with salt or potassium.
Can I Flush The Toilet When My Water Softener Is Regenerating?
Yes, you can flush the toilet during a water softener’s regeneration. It won’t disrupt the process. Just be mindful that water pressure might be lower.
How Does A Water Softener Work?
Water softeners remove minerals such as calcium and magnesium from water using resin beads, a process known as ion exchange.
What Is A Water Softener?
Water softeners remove minerals like calcium and magnesium from hard water, making it soft.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanics of water softeners is essential for any homeowner dealing with hard water issues. This step-by-step guide has walked you through the process, from the initial water analysis to the rejuvenation of resin beds. Implementing this knowledge can lead to longer appliance life and more enjoyable water usage.
Remember to maintain your system regularly to ensure it continues to provide soft water efficiently.

Leave a Reply